IDF学会の報告
学会の発表を気にかけてくれていた方が多かったので、発表の一部を乗せることにしました。今回は、細かいデータ解析までは至らず、問題提起をしてきただけです。今後、何らかの形でデータ解析していき、論文にしていこうと思っています。
Early Insulin Spike and Associated Hypoglycemia (Relationship with Diabetes Development)
Kyoko Hirai1, Junichi Takahashi2, Shigenori Kominami3, Kairyu Go4
1 HIRAI Clinic, Japan ; 2 Joto Central Hospital, Japan ; 3 Kominami Hospital, Japan ; 4 Go Clinic, Japan
Results
Of 120 people investigated, there was a 30 minute insulin peak observed in 39 subjects. There was a 60 minute insulin peak observed in 52 subjects, there was a 120 minute insulin peak was observed in 25 subjects. A diagnosis of diabetes was found in four people. IGT (Impaired Glucose Tolerance) was observed in 7 subjects. IFG (Impaired fasting glycemia) was observed in 0 subjects.
Method of Nutritional Guidance
In Hirai Clinic, nutritional guidance is offered not by nutritionists but by nurses who have detected impaired glucose tolerance (IGF) in patients. This is because it is considered that many nutritionists tend to have studied nutrition with an academic objective and may not be able to provide practical nutritional guidance that is applicable in real life. In the nutritional guidance given in Hirai Clinic, nurses propose a personalized improvement plan in respect to the individual patients lifestyle. They emphasize the importance of eating breakfast daily, referring to a typical Japanese breakfast similarly offered at Japanese-style inns.
Nurses advise patients to identify foods with a high animal fat so that patients can control the animal fat intake; the nurses describe high fat items as “thick”, “fluffy” and “crispy” foods that melt easily in your mouth. In addition, the nurses also instruct that patients do not always have to stay with three meals a day and should eat about 100 calories of food if they fall into a fasting state for long hours.
The minimum amount of each nutrient required per day is estimated based on the patient’s height. In order to improve the patients understanding about the importance of balanced diet, patients are given an opportunity to eat sample meals prepared by a Japanese restaurant. Through this process, patients enhance their understanding that a minimum balanced diet is critical to the treatment of preventing diabetes. Patients are also briefed on low glycemic index (GI) food.
Discussion
It is reported that early insulin spikes contribute to a reduction of blood triglyceride levels. However, hypersecretion of insulin is considered to ultimately lead to a decreased insulin secretion.
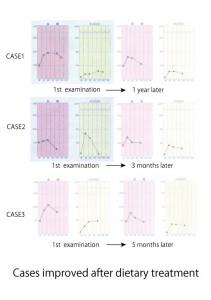
In cases where an insulin peak is observed in 30 minutes after a OGTT, patients may have time in the prevention of diabetes, but excessive, abnormal secretion of insulin should still be controlled. This is because excessive insulin secretion may cause hypoglycemia, which may result in glucotoxicity in such that patients tend to reach out for sweets. In cases where an insulin peak is observed in 60 minutes, patients may be suffering from constitutional delay of insulin secretion. In this case, patients may develop diabetes relatively quickly. It is necessary for such patients to understand their condition and be careful about their diet. In cases where an insulin peak is observed in 120 minutes, immediate action is required as patients are likely to develop diabetes in a short period of time.
World Health Organization states that macrovascular diseases are progressing even in the phase of IGT. Old methods of testing are more thorough than modern methods of testing for diabetes.Therefore treatment should be provided before patients experience IGT. Since IGT appears in diverse patterns, it is difficult to detect the condition at an early stage by means other than an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). Furthermore, it is challenging to give nutritional guidance to ethnic groups like Japanese who maintain an omnivorous diet. It is therefore necessary to provide personalized lifestyle guidance.